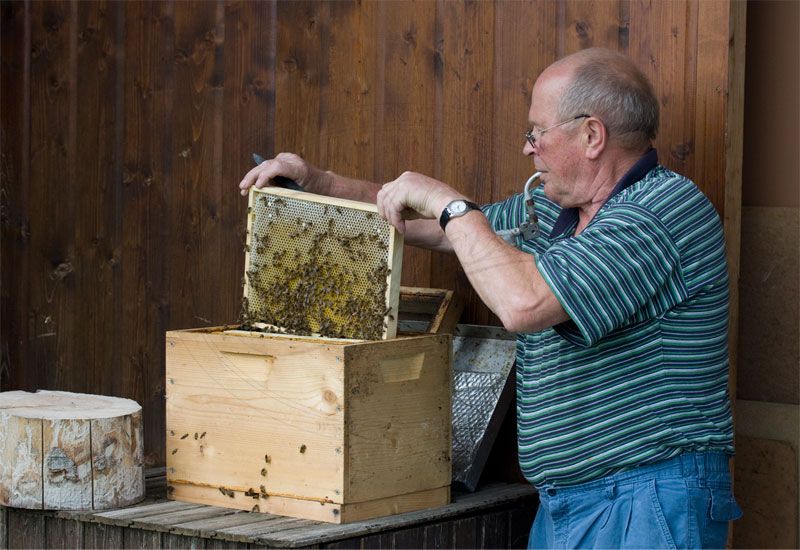
A look at the world without bees
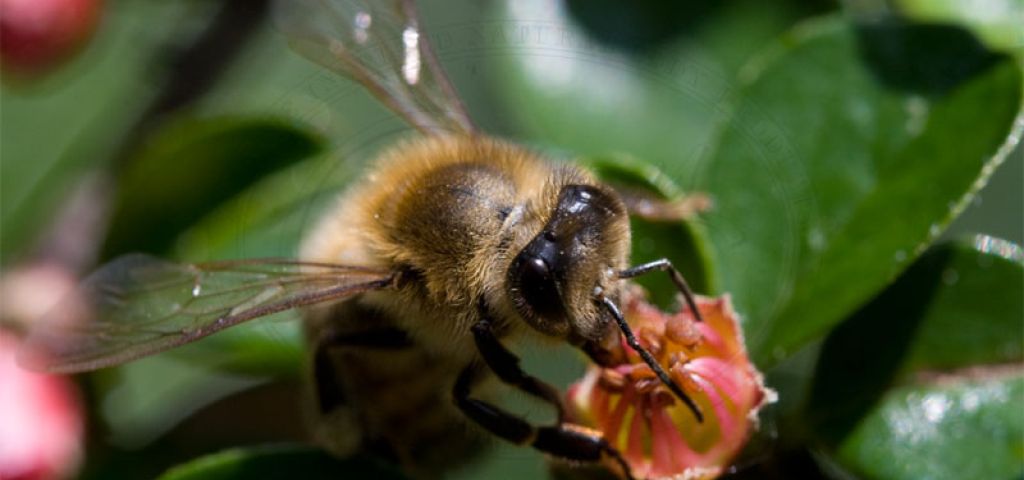

If the bee disappeared off the surface of the globe, then man would have only four years of life left. No more bees, no more pollination, no more plants, no more animals, no more man.
- Albert Einstein
What would the world be like if the bees disappeared?

Man would experience malnutrition as a lack of the essential vitamins and minerals needed from vegetables and fruits.
In the United States alone more than 800,000 hives have been wiped out in the year 2007.
What is the cause? Colony Collapse Disorder. The name was first given in late 2006 after beekeepers observed their bees dyeing off one colony after another.
Lets look into detail:
Man would experience malnutrition as a lack of the essential vitamins and minerals needed from vegetables and fruits.
In the United States alone more than 800,000 hives have been wiped out in the year 2007.
What is the cause? Colony Collapse Disorder. The name was first given in late 2006 after beekeepers observed their bees dyeing off one colony after another.
No bees means no cottons, no orchards, no vegetables, no forage crops, lack of bacon and steak cuts, no beef, no coffee, no fruit juice, no milk, no soy, no oranges, no grapes, no watermelons, no cucumbers, no apples, no almonds, no squash, no cherries, and certainly no honey. We would have to pollinate flowers ourselves and what hard work that would be.
Is the pesticide to blame? Sichuan province in China lost the entire population of their honey bees due to pesticides. Since the 1980's the people of Sichuan pollinate their trees by hand. Imagine holding bamboo sticks with chicken feathers attached at the end to them attempting to pollinate a pear tree.
The average person would complain of picking strawberries out of a field let alone pollinating single flowers by hand.
The world is not ready for the disappearance of bees. Educate those around you about the importance of bees and other insects as they are crucial and play a key role in pollinating wild flowers, our crops, fruits and vegetables. As sarcastic as it may sound without bees man would die.
The Life of a Bee
-
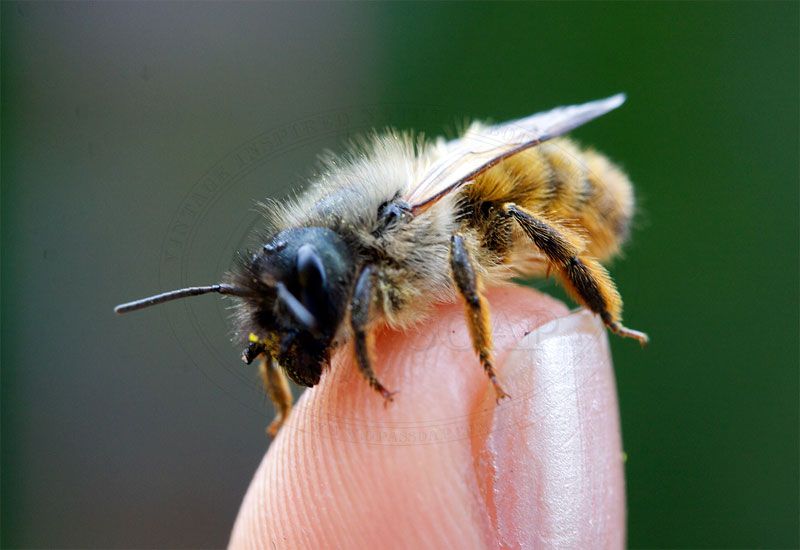
A Bee hive has between 30,000 and 80,000 bees
- There are 3 different bees in one hive
- Queen (fertile females) - The Biggest bee in the hive. (See Photo below #17)
- Regular Bee (sterile females) - (Worker Bee)
- Drones (males) - The Male Bee slightly larger than the regular bee but cannot sting.
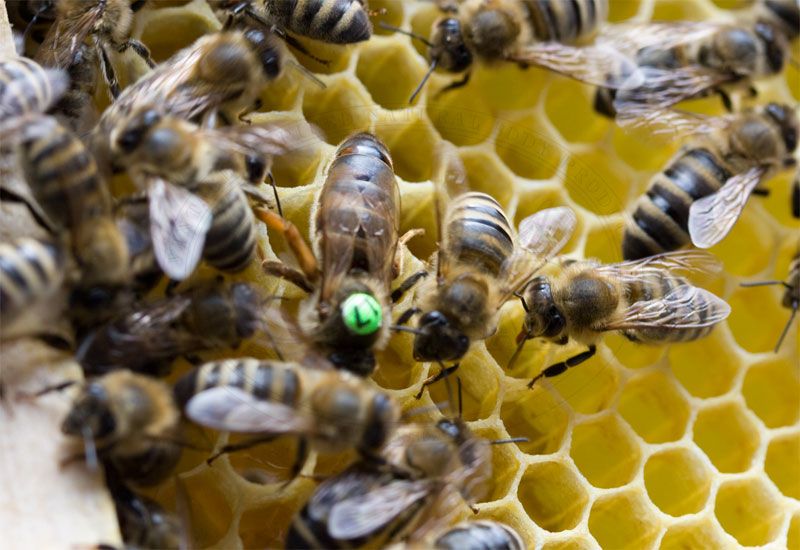



This precious bud-resin is collected by the industrious bees in the hive by chewing and in salivating, in result, propolis is processed.
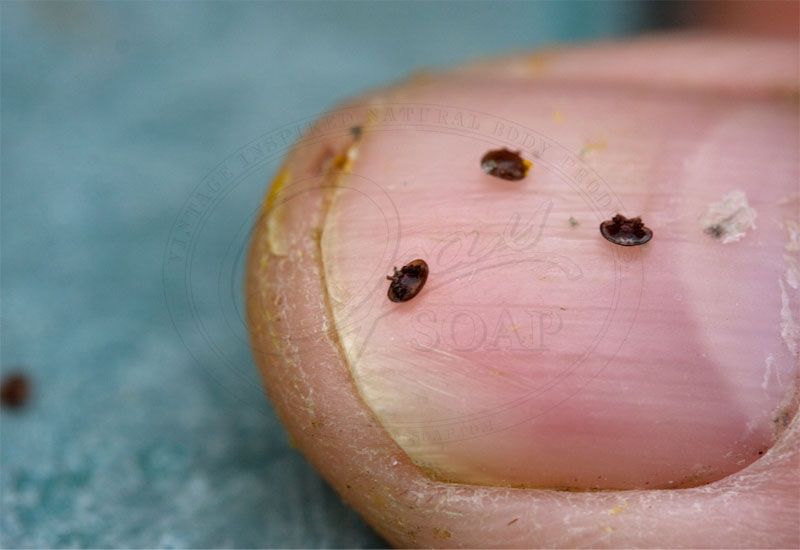
Natural Enemies of the bee
Varroa destructor, a mite that attacks honey bees.
The Varroa mite (Varroa destructor) is as a adult about 1.6 millimeters, which is set on the honey bee, like a leech bites in mammals, (to this in size relation, this would correspond to "a large loaf of bread" on a human head sucking blood). The actual development and reproduction of the mite is not in the adult bee, but instead in the capped brood.
What is a capped brood? A brood is the larval stage or pupil stage occurring 8 - 9 days after the egg has been laid that has been capped over in its cell.
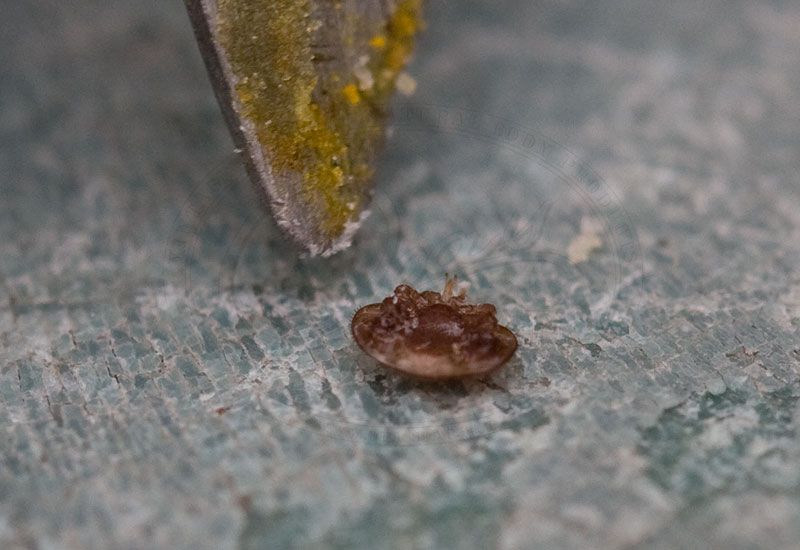

Therefore, it is in the Varroose (formerly Varroa jacobsoni) - how this parasite infestation is called - essentially a brood disease. In the winter months when no brood is cared for, the Varroa mite completely uses the adult bees to survive.
Royal Jelly
Resin - Propolis
- Propolis is the resinous substance by bees from the bark and buds of various plants, preferably trees.
- Propolis is used to seal the hive, both physically, in medical terms as against pathogens.
- The name "Propolis" means protector of the city (the beehive).
The colors of Propolis can range from; light yellow, brown, or black. Its taste is bitter and pungent, the odor usually sweet, but it will vary depending on origin. The layers you see are the different colors of the plants and flowers collected from the bees when pollinating.
At 15°C (60°F) Propolis is brittle and hard, smooth at 30°C (120°F) making it more sticky and very soft. From 65°C (150°F) it is liquid, but completely melts only at about 100°C (212°F).
Origin of Propolis
The bees gather propolis, the resinous preferably on the buds of various trees such as poplars, willows, aspen and horse chestnuts. These buds of the tree leaves contain a protective casing of a balmy fragrant waxy resin (cutin). You can use poplar bud resin protection under this way directly for medicinal purposes and for anointing.
This precious bud-resin is collected by the industrious bees in the hive by chewing and in salivating, in result, propolis is processed.
Use of Propolis in the hive
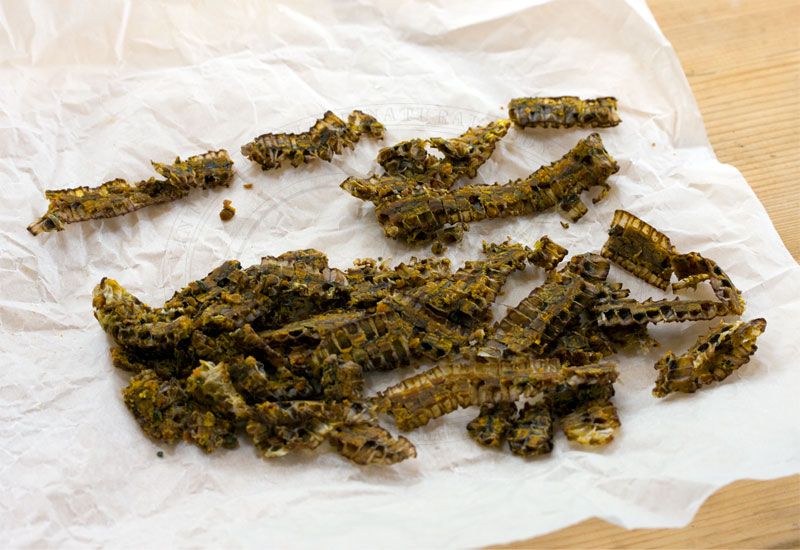
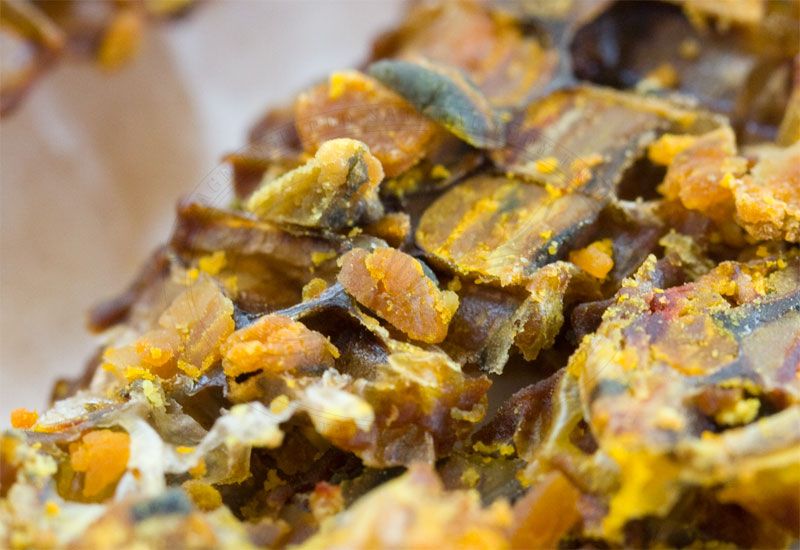
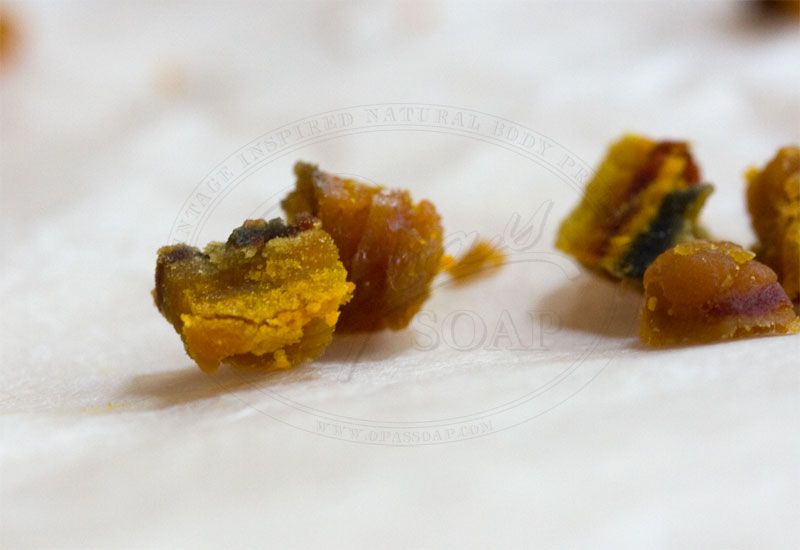
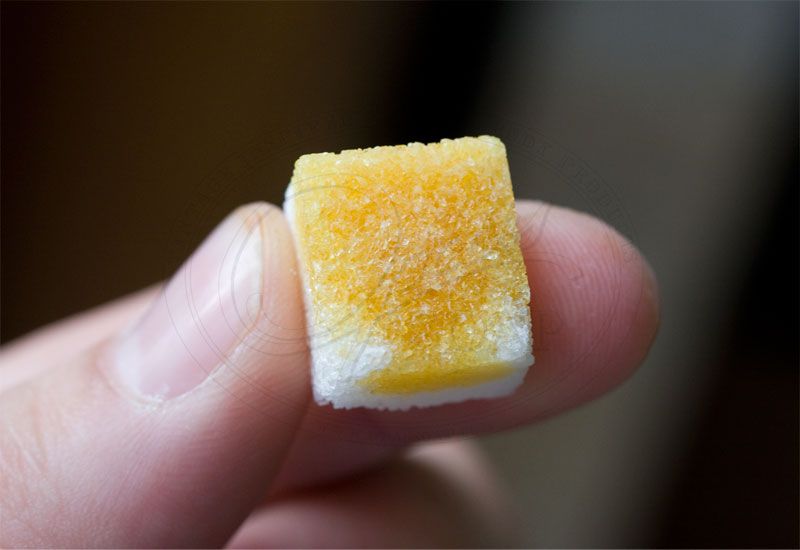





Ingredients of Propolis
Gradually, more and more ingredients in the propolis are discovered. Researchers still are not finished with the complete analysis of the ingredients.
Since propolis according to the origin of the raw material (species) are designed very differently, it is in the following incomplete list with approximate values.
Propolis Ingredients
-
50% resins
- 30% wax
- 10% essential oils
- 5% pollen
- 3% organic matter
- 2% minerals
Organic and mineral substances
- Vitamins
- Vitamin A
- Vitamin B3
- Vitamin E
Organic secondary plant substances
- Flavonoids
- Flavone
- Antibiotic substances
- Caffeine acid
- Benzylkumurat
- Tannins
- Salicylic acid
- Pinocembrin
- Pinobanksin
- Galangin
- Quercinin
- Apigenin
- Halangin
- Ruthin
Trace elements
- Iron
- Calcium
- Cobalt
- Copper
- Magnesium
- Manganese
- Selenium
- Silicon
- Zinc
Have you a clue?
- It takes about 2 million visits to flowers to make one pound of honey!
- One hive travels about 55,000 miles to gather one pound of honey!
- The bee gathers a good teaspoon full of honey in its lifetime.
- It takes about 1500 Flowers to gather one load of pollen.
- The bee has 4 wings.
- The lifespan of a bee is aprox. 35 - 45 days.
- A Queen can live up to 5 years. Most beekeepers re-queen once a year.
- A beehive can have 30,000 - 80,000 bees. This drops significantly during the winter months.
Find your local beekeeper's pollen and honey.
Not only will you support your local businesses, but it can also help you with allergies and irritants. Bees in your area will collect your local plants pollen that will help your immune system.
When a bee collects pollen, pollen spores are left in the honey. Pollen is what causes allergy sufferers to sneeze or experience watery and itchy eyes. By ingesting local honey you can fight plant allergies because you are vaccinating your self (Immunotherapy) adding pollen to your body which builds a stronger defense and becomes immune to the plants and flowers around you.
Here is a link to pbs podcasts about bees.
Thank you to beekeeper (Imker) Alfred Vitztum in Austria. Valuable information was received from Mr. Vitztum to write this article along with research.
Please also visit and support your PBS Station.