Birth control pills = poison
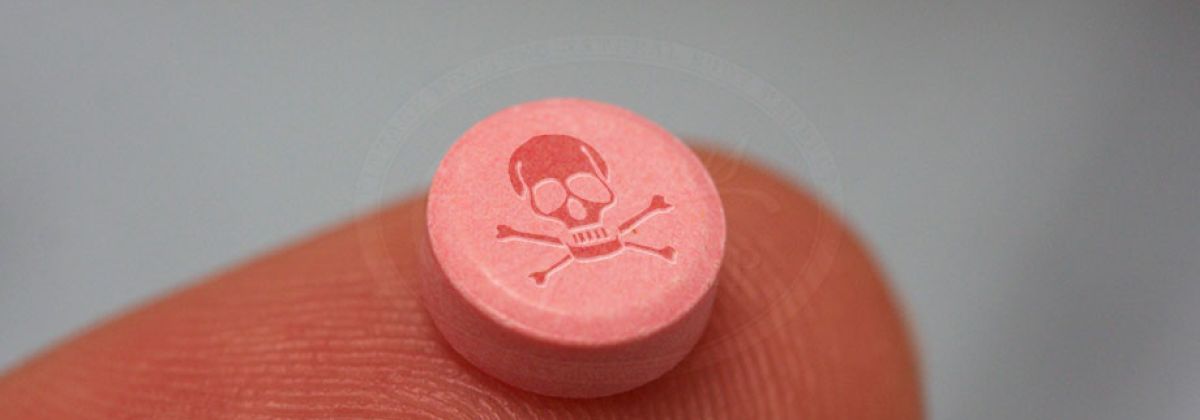
The side effects included: Nausea, Blurred Vision, Bloating, Weight gain, Depression, Blood clots, Strokes
Many women complained about the contraceptive pill, their complaints were dismissed in the early 60's and 70's. Later in the 1980's a lower dosage of progesterone in the pill would be introduced to the public. The new pill - would have as little as one milligram of progesterone.
Oral Contraceptive options are great to have and some do work effectively but they do have risk for women and studies have linked them to cause Migraines, PMS, Breast Cancer, Heart Disease, Heart Attacks, Strokes, Blood Clots, High Blood Pressure, Uterine Cancer, Infertility, Depression, Post-Partum Depression, Uterine Fibroids, Anxiety Disorders and Hysterectomies.
Contraceptive pills contain two synthetic hormones, estrogen and progestins. These synthetic hormones are similar if not identical to the hormones female ovaries make. The synthetic hormones prevent the ovaries from releasing it's egg then thickens the cervical mucus preventing the sperm from implanting the egg itself. You can achieve this by making the body think it's pregnant.
What is estrogen and what role does it play?
Natural estrogen is a group of hormones of E1, E2, and E3. E1 or Estrone is a dominant hormone during menopause and is commonly found in the urine, ovaries, and placenta. Estrone is produced in small quantities by the stromal tissues of the ovaries. After menopause, estrone increases, possibly due to increased fat. The more estrone one has, the higher risk of breast cancer.
E2 or Estradiol is the most active and potent form of estrogen, and is responsible for over 400 functions in the female body. E2 is the primary estrogen produced by the ovaries. Estradiol is most abundant in young women in their teens and twenties and is important in helping women look and feel young. E3 or Estriol is the weakest and least active estrogen. High levels of estriol are produced by the placenta during pregnancy and protect the body against forms of cancer.
You may test until the end of time, but no synthetic or chemically made pill can replace our natural hormones without having no side or damaging effects permanently or temporary. You are putting synthetic hormones into your body. Our bodies function the same way they have always and it knows the difference between the natural hormones it makes versus the foreign synthetic hormones being pumped into the body.
The synthetic progestin in oral contraceptives will often cause your ovaries to stop producing natural progesterone because it recognizes the synthetic progesterone being flooded into the system.
This shut down causes an imbalance resulting in more estrogen and no progesterone.
What happens when you have no progesterone?
How can I stop this and replace my progesterone?
First, stop using your oral contraceptive. There are some ways to produce natural progesterone. Please note natural progesterone will not be produced by the body with missed ovulations or after menopause.
- Include protein in your diet with no antibiotics or growth hormones.
- Consume whole grains, fruits and vegetables.
- Take up a physical activity 3 times per week. (Exercise helps balance hormones, increases libido)
For those after menopause, there are natural progesterone creams on the market. After conducting some research, some women are happy with their results. They have claimed progesterone creams have helped with hot flashes and mood swings.